What is an SSL certificate for a website? what are the different types of SSL certificates? and which one is perfect for your website? make sense a lot for your website security. That’s why today we’ve come up with our detailed and informational blog to help you secure your website.
Your website needs an SSL certificate to keep visitors’ confidential information private, get consumers’ trust, verify ownership of the website, prevent hackers from creating a fake version of your site, improve search ranking, and reduce bounce rate.
The SSL certificate moves your website from HTTP to HTTPS which is a more secure version. And “S” in the HTTPS stands for “Secure“. To put it simply, your website will be more secured with the SSL certificate.

Table of Contents
What is an SSL Certificate?
The SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates create an encrypted connection between a web server (website) and a browser (user). They are small data files installed on the website’s origin server that contain the identity of the website owner (organization or business), the website’s public key, a digital signature of CA (Certificate Authority), and more relevant information.
The encrypted connection ensures that all the data transferred between a web server and a browser remain private and safe.
Once you’ve installed an SSL certificate on your website, a padlock icon next to the URL of your website will be displayed and your website HTTP version will be moved to the HTTPS version.
Why Do You Need An SSL Certificate For Your Website?
Installing and activating an SSL certificate on your website is not only important in securing your website but also a very important step in building your website.
#1. Protect Your Website
The websites with SSL certificates are marked as secured websites on all browsers. The browsers have registered all websites without SSL certificates as non-secure websites.
To check that a website is secured or not secured, click the padlock icon (or ℹ️ icon) in the address bar of the website.
#2. Visitors Trust SSL-activated Website
Google warns the users when they visit a website that hasn’t installed the SSL certificate and marks it as a non-secure website. Users can visit that website but most times they leave it.
Consumers and customers trust websites and purchase products from online stores that have installed SSL certificates. Because they believe that their name, password, mobile number, and bank account details are secured with them.
#3. Enable HTTPS Version
Installing an SSL certificate moves your website from HTTP to HTTPS which provides the website security. The “S” in HTTPS means Secure and HTTPS is the combination of Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure with SSL certificates.
#4. Google’s Ranking Algorithm Factor
Although the purpose of an SSL certificate is to create an encrypted connection, it also boosts the SEO of your website.
The SSL certificate is part of Google’s searching ranking algorithm, according to Google Webmaster Trends Analysts. This means that Google gives priority to SSL-enabled websites.
#5. SSL-enabled Websites Load Faster
The browsers allow you to access websites without SSL certificates. But SSL-enabled websites load faster than other websites that haven’t installed SSL certificates.
#6. Reduce Bounce Rate
If an SSL certificate isn’t installed on your website, users will click the link of your website, (as your website is marked as non-secure), then they’ll leave your website and will go elsewhere. In fact, this increases the bounce rate.
To reduce the bounce rate and get more benefits, you must install an SSL certificate on your website.
How Does SSL Certificate Establish A Private Connection?
When a browser attempts to visit a website (the website has installed an SSL certificate), the web server and browser create an encrypted connection utilizing a process called SSL Handshake. This process occurs promptly and is invisible to users.
Three keys are used to create an encrypted connection: the private, public, and session keys. The public and private keys get together during the SSL Handshake to produce a symmetric session key. And once the SSL connection is established, the session key is used to encrypt all transferred data.
Quick Note: Anything encrypted with the public key can only be decrypted with the private key.
What Are The Different Types Of SSL Certificates?
The umbrellas that SSL certificates fall under are validation and domain numbers. Both have three categorizations that can be applied to SSL websites.
The single, wildcard and multi-domain SSL certificates are available to cover a specific number of domain names. And the domain, organization, and extended validation are available for encryption and validation of SSL certificates.
#1. Single Domain SSL Certificates
This SSL certificate covers only a single domain name (but does not authenticate its subdomains).
For instance, if RealBSG.com has a single domain SSL certificate, then it cannot be used to verify its subdomains (community.realbsg.com) or another domain name. It just covers all pages on RealBSG.com.
#2. Wildcard SSL Certificates
A Wildcard SSL Certificate secures a single domain name and its subdomains. For example, this SSL certificate authenticates yourdomain.com and its subdomains like blog.yourdomain.com, community.yourdomain.com, and shop.yourdomain.com.
#3. Multi-Domain SSL Certificates
As the name shows, a multi-domain SSL certificate covers multiple domain names under one roof like sending several letters in a single envelope.
To protect several domains (like yourdomain.com, 2nddomain.com, and example.com) using an SSL certificate, you need a multi-domain SSL certificate.
#4. Domain Validation (DV) Certificate
This certificate is the cheapest yet trusted level of domain validation and delivers a low level of encryption.
To get this SSL certificate for your website, you must prove that you own the website (domain). You can prove this by adding DNS records linked with your domain or sometimes you have to send an email to a Certificate Authority (CA).
The domain validation certificate is the right choice for those websites that don’t sell products or services on their websites like blogs, portfolio websites, and small businesses.
#5. Organization Validation (OV) SSL Certificates
The organization validation SSL certificate enables a medium level of encryption. This certificate verifies that the organization and domain name are authentic. On the browser, visitors would see the padlock icon, the organization’s name, address, and HTTPS in the URL bar.
To get this validation SSL certificate, you have to request CA (Certificate Authority) and then they will investigate for issuing the certificate.
#6. Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificates
The extended validation SSL certificates are the most expensive and trustworthy. This certificate displays the padlock, business name, business country, and HTTPS in the address bar.
You have to request CA to obtain this certificate. Then the CA will check the full background of your business (does your business exists and is registered as a business) and also you’ll prove that you are authorized to own the domain.
This certificate ensures users that you are legally allowed to collect the users’ data.
How To Get An SSL Certificate For My Website?
Firstly, you need to know what type of SSL certificate works best for your website. For most websites, the standard SSL certificate is the ideal solution. But if your content is published on separate domains or subdomains, then you need a different type of SSL certificate.
Once you’ve chosen the right type of SSL certificate, then you need to obtain it from a Certificate Authority (CA). A Certificate Authority is a trusted third party that makes SSL certificates. The CA will digitally sign the SSL certificate with their own private key and enable client devices to verify it.
SSLs.com is the trusted Certificate Authority that offers you SSL certificates at the cheapest price on the market.
Most CAs charge a fee for issuing an SSL certificate but also you can get it for free. Once the CA has issued the certificate, then install the certificate on the website’s origin server. Most web hosts like Bluehost, InMotion Hosting, HostGator, Interserver, and Nexcess offer you free SSL certificates with hosting services.
Once the SSL certificate has been installed, users would see the padlock icon and HTTPS in the address bar.
How To Tell If A Website Has An SSL Certificate?
When you visit a website with an SSL certificate, you would see some differences in the address bar.
#1. Padlock Icon In Address Bar
All websites with SSL certificates have a padlock icon in the address bar. Once you click on the padlock, you’ll see more relevant information about the website and Certificate Authority.
#2. HTTPS Version
If you visit a website’s URL starting with HTTPS, it means that the website has installed an SSL certificate.
#3. The Certificate Is Valid
If a website requests more information, you should check whether the website’s SSL certificate is valid or expired.
To check that the SSL certificate is valid or expired, simply click Ctrl + Shift + I simultaneously.
Or if you want to do it manually, then follow these steps.
- Click “three dots (⋮)” from the right upper corner in the Chrome browser.
- Then move your mouse cursor to “More tools“, and there will open another menu.
- Click “Developer tools” from that menu.
- Finally, navigate to the “Security” tab where you see whether the SSL certificate of the website is valid or expired.
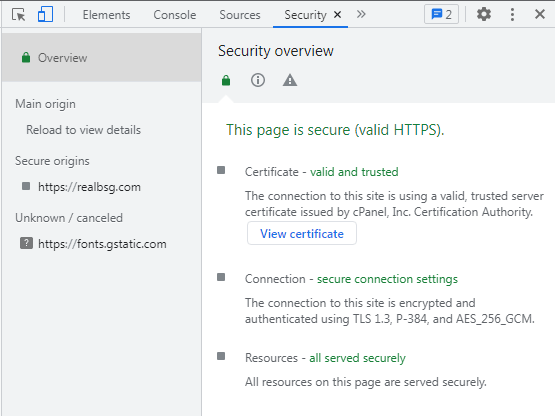
Note: Even If a website displays the HTTPS and padlock in the URL bar but its SSL certificate could still be expired. That’s why you should check the validation of the SSL certificate.
Conclusion
An SSL certificate is a small data file (installed on the website’s origin server) that establishes an encrypted connection between a browser and a web server.
The SSL certificate is used to keep the users’ data private, provide security for online communications, protect the website from hackers, authenticate the ownership of the website, and deliver trust to users.
The 6 different types of SSL certificates are single SSL certificates, wildcard SSL certificates, multi-domain SSL certificates, domain validation SSL certificates, organization validation SSL certificates, and extended validation SSL certificates.
So what are you waiting for? get a perfect SSL certificate for your website at the cheapest price on the market.
Read More:


